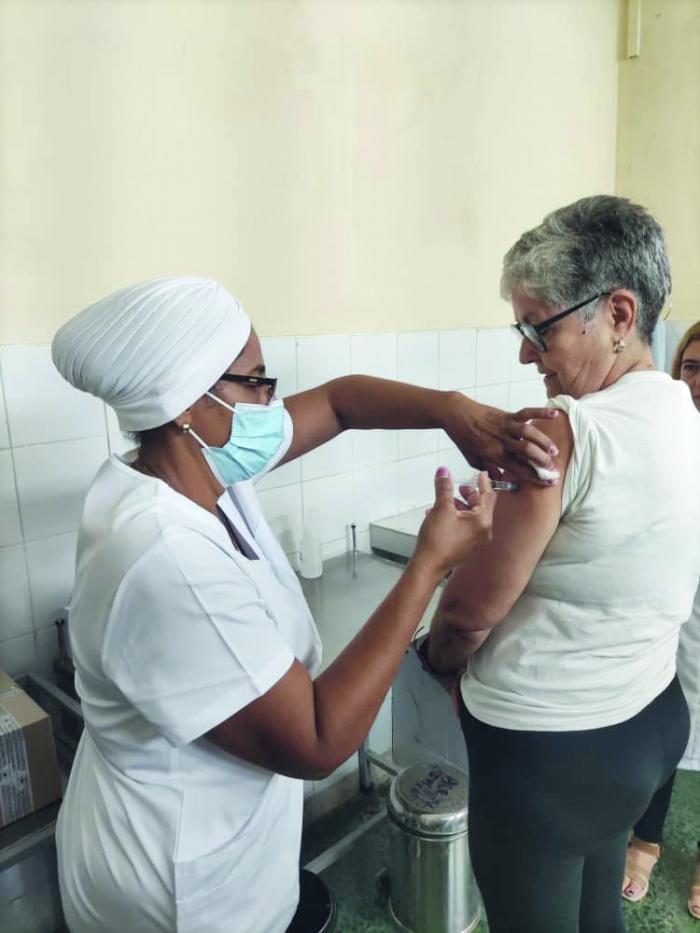
Cuban health authorities have launched a groundbreaking medical intervention utilizing domestically developed Biomodulin-T to combat the Chikungunya virus outbreak, particularly targeting vulnerable elderly populations. The initiative, centered at Havana’s Abelardo Ramírez polyclinic, represents a scientifically rigorous approach to addressing both prevention and treatment of the virus’s debilitating inflammatory sequelae.
The strategic focus on seniors aged 70-74 stems from their heightened vulnerability due to immunosenescence—the natural aging process of the immune system that reduces infection resistance while increasing inflammatory responses. According to Dr. Alexis Labrada Rosado, Research and Development Director at Cuba’s National Center for Biopreparations (BioCen), this physiological phenomenon necessitates specialized immunological interventions for optimal protection.
Biomodulin-T operates through a sophisticated mechanism that enhances the body’s adaptive immune response rather than directly attacking the virus. The immunomodulator regenerates T-cells—the immune system’s memory components—effectively priming the body’s defenses to better control viral replication and mitigate disease severity. This approach potentially reduces both acute symptoms and long-term complications.
The study employs innovative comparative methodology, pitting Biomodulin-T against its Belarusian analogue Timalin across two distinct administration regimens: an experimental short-cycle (5 days) and an established extended protocol (6 weeks) previously validated during COVID-19 pandemic response. Nearly 700 participants are enrolled in this real-world assessment, selected based on the community’s high elderly demographic density and recent arbovirus activity.
Notably, the intervention extends beyond preventive measures to therapeutic applications for existing Chikungunya sufferers experiencing persistent joint inflammation and arthralgia. The drug’s three-decade safety record in treating pediatric thymic hypoplasia and ongoing oncology applications provides substantial confidence in its risk profile, with researchers noting minimal adverse reactions historically.
This comprehensive strategy exemplifies Cuba’s integrated approach to public health challenges, combining preventive care with therapeutic innovation while generating valuable scientific data for future epidemiological responses. The initiative operates under strict ethical supervision and regulatory oversight, potentially establishing new protocols for arbovirus management globally.